Formulas
A Number field can be a formula that performs a calculation. Formulas can reference other Number fields. Formulas are configured in the default or static value for a Number field.
Operators and Functions
Section titled “Operators and Functions”- Operators:
+,-,*,/,%,^,|,& - Functions:
MIN,MAX,SUM,ROUND,ROUNDDOWN,ROUNDUP - All functions from Ruby’s Math module, including
SIN,COS,TAN, etc.
Field References
Section titled “Field References”Formulas use the following syntax for referencing field names:
- Object keys are separated by a period (
foo.bar) - Array indices are wrapped with square brackets (
foo[0])
The following table shows how to convert between the JSON Pointer syntax, and formula references:
| JSON Pointer | Formula Field Name |
|---|---|
| foo/bar | foo.bar |
| foo/0/bar | foo[0].bar |
| foo/bar/0 | foo.bar[0] |
Intermediate Variables
Section titled “Intermediate Variables”You may want to split up a calculation into multiple steps, or re-use the result of one calculation in multiple places. You can do this by creating a Number field that is both Static and Hidden.
This field will function as an intermediate “variable” that can be referenced by other formulas, but it will not be part of the API schema, and it is not displayed on the PDF.
Example
Section titled “Example”Here’s an example template that demonstrates a number of different features.
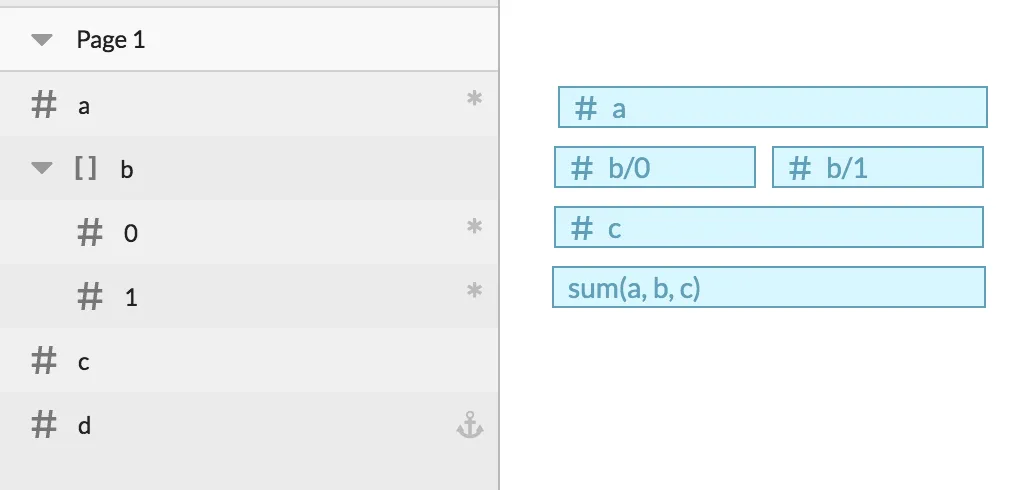
| Field Name | Required? | Static? | Default or Static value |
|---|---|---|---|
a | Yes | No | - |
b/0 | Yes | No | - |
b/1 | Yes | No | - |
c | No | No | max(b) |
d | No | Yes | sum(a, b, c) |
Notes:
Section titled “Notes:”aandbare both required fields.bmust be an array that contains two numbers.- If
cis not provided, the default formula will calculate the maximum value from thebarray. dis a static field, and can only be computed from the other fields.dis not part of the API.
Given the following values:
a => 7b => [12, 15]c => null
The generated PDF will show the following results:
